Drug delivery systems in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis, a systematic review of in vivo studies
What we know so far
Knee osteoarthritis (OA) affects around 250 million people worldwide, making this pathology one of the leading causes of disability. Current treatment approaches for OA as weight control, adequate sport activity, oral, topical and intra-articular pharmacological treatments fail to control symptoms in 78% of patients. To overcome this failure new drug delivery systems have been developed in order to achieve a sustained release of the drug inside the joint.
Aim of the study
We wanted to investigate the state of the art of drug delivery systems for knee osteoarthritis. In order to do so we performed a systematic review of the literature using the following inclusion criteria: employment of a drug delivery system for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis, in vivo study and knee intra-articular (IA) route of administration.
Progress and prospects
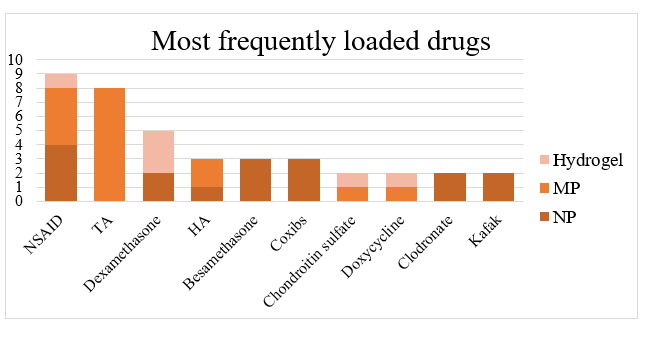
The most frequently used materials to create these drug delivery systems were polymers in particular PLGA, and the most frequently loaded drug category was represented by corticosteroids (16 studies), followed by NSAIDs (9 studies). This is due to their possible application as biomaterial for bioprinting. Concerning the choice of NP as most commonly employed drug delivery system, a number of reasons can be proposed. Firstly, the experience with NP in other fields as cancer therapy helps researchers to design NPs to reach particular tissue, cellular or molecular targets. The uptake of nanostructures by cells is higher than that of microstructure (1 and 10 µm) and NP are phagocytized more effectively by macrophages than microspheres. Nevertheless, hydrogels have a robust advantage upon other the other drug delivery systems. Concerning the advances in the drug delivery systems for knee OA, microparticles made of PLGA and loaded with Triamcinolone acetonide seem the closest attempt to make it to the clinical practice. This assumption stems not only from the fact that it was the most common combination used, moreover it was the subject of study of all the 4 studies performed on humans.
Acknowledgements: Prof. Elizaveta Kon, Fernando Torres Andón MD, Aldo Ummarino MD, Virgilio Program
Presented at: 9th Virtual European MD/PhD Conference on April 22nd, 2021.
Francesco Manlio Gambaro - Virgilio Program Student, Humanitas University, Italy