Focus on Lab: Humanitas Advanced Image Analysis Lab
The Advanced Image Analysis Lab under the leadership of Prof. Chiti, part of the Diagnostic Imaging Department, is an integrated facility dedicated to image analysis and research.
The lab deals with innovative approaches to identify novel image-derived biomarkers to characterize lesions, quantify tumor heterogeneity, and predict outcomes. Different approaches including radiomics, machine and deep learning are used to identify and/or describe specific biological properties of tumors using medical imaging.
The research team is working on some projects on lung cancer and other chest diseases, lymphoma, thyroid cancer, and liver disorders.
Specifically, projects on chest aim to:
- identify and classify (benign vs malignant) lung nodules on non-contrast enhanced CT images trough deep learning algorithm;
- assess the role of radiomics and artificial intelligence, circulating tumor DNA and their combination in staging, risk stratification, and outcome prediction of lung cancer;
- test the impact of different reconstruction algorithms on PET-derived radiomic features, and assess their clinical impact;
- provide an automatic description of chest radiograph;
- automatically diagnose and follow-up of COVID19 pneumonia on CT images trough deep learning algorithm.
Projects on lymphoma aim to:
- identify intra-patients lesions’ similarity and to predict the final outcome by baseline FDG-PET/CT images;
- correlate changes in disease tumor burden (total metabolic tumor volume), circulating tumor DNA evolutionary track, and response to immunotherapy.
Projects on thyroid cancer and liver aim to identify image-derived biomarkers to predict:
- patients’ outcome at baseline;
- liver disfunction at baseline in patients treated with surgery.
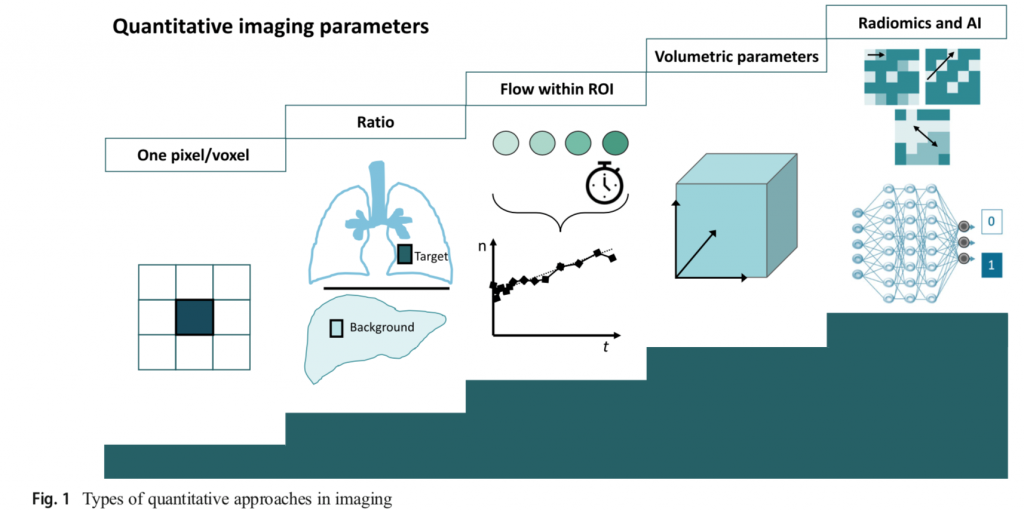
The group in the last years has focused the research activity on radiomics and artificial intelligence approaches. These approaches offer the advantage to explore and non-invasively assess biological tumor’s behavior by medical imaging. Radiomics extracts tens-to-thousands parameters through mathematical methods with increasing levels of complexity to describe the tumor’s heterogeneity as a function of the relationship between pixels or voxels within a region of interest. Artificial intelligence relies on the application of end-to-end algorithms that identify relevant features within an image as part of the learning process. The possibility of extracting an "imaging biopsy" using texture analysis and machine and deep learning approaches is one of the most promising and challenging fields of modern diagnostic imaging.
Follow our posts by leading researchers from Prof. Chiti's team for novel insights into the application to medical imaging of these new technologies.
Martina Sollini – Researcher and Virgilio Program Tutor
Image-derived biomarkers
What We Know So Far
Biomarkers are “measurable and quantifiable biological parameters (...) which serve as indices for health- and physiology-related assessments”.
The main advantage of the use of biomarkers lies in the fact that they are, or should be, easier and cheaper than direct measurement of the clinical endpoint. Three crucial aspects—high reproducibility, a sizeable signal-to-noise ratio, and a swift change in response to events (e.g., treatment)—make a biomarker good. In this regard, biomarkers derived from images have the potential to be among the most suitable.
Aim of the studies
The identification and validation of reliable image-derived biomarkers are crucial to address unmet clinical needs and to personalized patient management.
Progress and Prospects
We recently proposed some image-derived biomarkers based on radiomics and deep learning algorithms in different clinical settings, including primary lung cancer, thymic neoplasms, lymphoma, and thyroid lesions.
The project focused on thyroid cancer has been funded within the TRANSCAN-2 Joint Transnational Call 2017 (“PREDICt - Profiling radioREsistant Differentiated thyroid Cancer: genes, immunity, cancer stem cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition”).
Read our articles on image-derived biomarkers
- Kirienko M, Sollini M, Silvestri G, Mognetti S, Voulaz E, Antunovic L, Rossi A, Antiga L, Chiti A. Convolutional Neural Networks Promising in Lung Cancer T-Parameter Assessment on Baseline FDG-PET/CT. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2018 Oct 30;2018:1382309. doi: 10.1155/2018/1382309. eCollection 2018.
- Kirienko M, Cozzi L, Rossi A, Voulaz E, Antunovic L, Fogliata A, Chiti A, Sollini M. Ability of FDG PET and CT radiomics features to differentiate between primary and metastatic lung lesions. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2018 Sep;45(10):1649-1660. doi: 10.1007/s00259-018-3987-2.
- Kirienko M, Cozzi L, Antunovic L, Lozza L, Fogliata A, Voulaz E, Rossi A,Chiti A, Sollini M. Prediction of disease-free survival by the PET/CT radiomic signature in non-small cell lung cancer patients undergoing surgery. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2018 Feb;45(2):207-217. doi: 10.1007/s00259-017-3837-7.
- Kirienko M, Ninatti G, Cozzi L, Voulaz E, Gennaro N, Barajon I, Ricci F, Carlo-Stella C, Zucali P, Sollini M, Balzarini L, Chiti A. Computed tomography (CT)-derived radiomic features differentiate prevascular mediastinum masses as thymic neoplasms versus lymphomas. Radiol Med. In press. doi: 10.1007/s11547-020-01188-w
- Sollini M, Kirienko M, Cavinato L, Ricci F, Biroli M, Ieva F, Calderoni L, Tabacchi E, Nanni C, Zinzani PL, Fanti S, Guidetti A, Alessi A, Corradini P, Seregni E, Carlo-Stella C, Chiti A Methodological framework for radiomics applications in Hodgkin’s lymphoma. European J Hybrid Imaging 2020;4:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41824-020-00078-8
- Sollini M, Kirienko M, Magnoni P, Cozzi L, Di Tommaso L, Lania AG, Chiti A. [18F]FDG-PET/CT texture analysis in “hot” thyroid nodules: results of the validation cohort. Biomed J Sci & Tech Res. 18(2)-2019. doi: 10.26717/BJSTR.2019.18.003110.
- Sollini M, Cozzi L, Pepe G, Antunovic L, Lania A, Di Tommaso L, Magnoni P, Erba PA, Kirienko M. [(18)F]FDG-PET/CT texture analysis in thyroid incidentalomas: preliminary results. Eur J Hybrid Imaging. 2017;1(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s41824-017-0009-8.
About the Authors
Martina Sollini
Researcher and Virgilio Program Tutor
Full Professor, Virgilio Program Mentor
Director of Department of Biomedical Science
Unit Director Nuclear Medicine Department at the Humanitas hospital